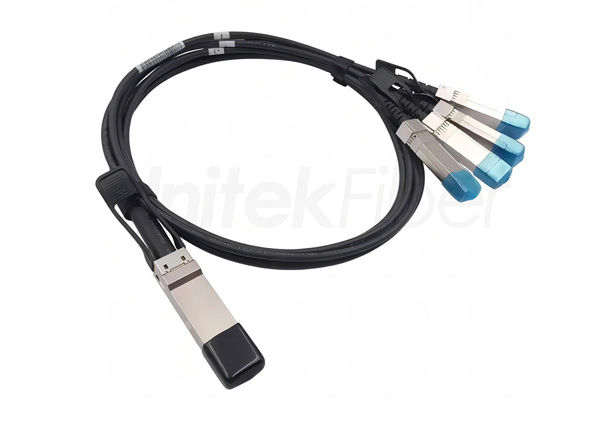
Data centers are the nerve centers of modern information society, responsible for the rapid processing and secure storage of massive amounts of data. In this context, Active Optical Cables (AOCs) and Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are particularly crucial in data center applications. They act as the bridge for data transmission, ensuring high-speed and stable connections between servers, storage devices, and other network equipment. By using Active Optical Cables (AOCs) and Direct Attach Cables (DACs), data centers can achieve efficient data exchange and meet the ever-growing data processing demands. The following will provide a detailed introduction to the application of Active Optical Cables (AOCs) and Direct Attach Cables (DACs) in data centers.
The internal network of a data center is typically divided into three to four layers from bottom to top. Various interconnections exist between these layers, from the servers to the core network, with lengths ranging from a few meters to several kilometers. Therefore, different data transmission technologies and interface standards are required.
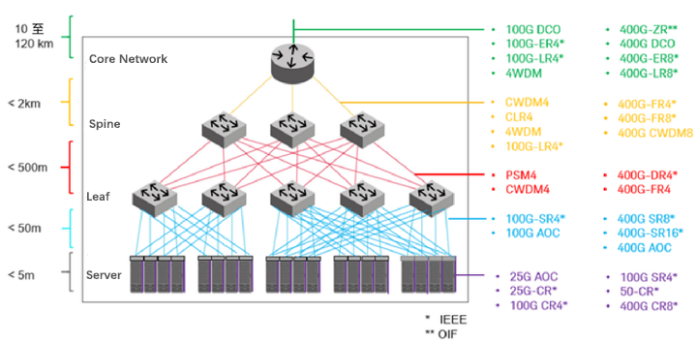
Top-of-Rack (TOR) switch for server cabinets/racks –The bottom layer of server racks is connected to the TOR switches at the top of the cabinet. Today's data centers typically deploy 25G-40G networks, with some artificial intelligence (AI) applications using 100G-200G speeds. Connections are either within the cabinet or between adjacent cabinets, typically over distances of no more than 5 meters. Typical interface technologies currently used include direct attach copper (DAC) and active optical cables (AOCs). As speeds increase to 400G and 800G, the data transmission distance of direct attach cables (DACs) becomes too short, requiring a switch to active electrical cables (AEC).
TOR switch to leaf switch – The Layer 2 interconnection is the connection between the TOR switch and the leaf switch. This interconnection has a transmission distance of up to approximately 50 meters.
Leaf-to-Spine –Leaf-to-spine connections offer connection distances of up to 500 meters and can be used within a single campus or across multiple adjacent campuses. This data transmission technology utilizes interface speeds similar to those used in top-of-rack (TOR) switch to leaf switch connections, with 400G switches being the mainstream in data centers.
Spine to Core Network – When the transmission distance further increases to 2 kilometers, users begin to consider the cost of fiber optics. Therefore, wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology is typically used to transmit data over a single fiber using different wavelengths of light signals. Currently used modules include 100GBASE-LR4, 100G-CWDM4, and 400GBASE-ER4/-LR4/-FR4, among others.
Data center interconnect (DCI) – is a data transmission method typically used to connect adjacent data centers, enabling load balancing or disaster recovery backup. Transmission distances can range from tens to hundreds of kilometers. Longer distances utilize dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) technology, and in recent years, coherent communication has replaced direct detection technology. For many years, telecommunications operators have deployed 100G coherent technology in long-distance (hundreds of kilometers) applications. They are also researching how to increase speeds to 200, 400, and 800G. DCI transmission distances are not as long as those in telecommunications applications, primarily involving point-to-point transmission, allowing the use of smaller, lower-power pluggable modules (such as 400G-ZR) for coherent transmission.
DAC Cables are generally translated as direct cables or direct-attach copper cables. They are typically purchased as cable assemblies of fixed lengths with fixed connectors at both ends. The ports are not interchangeable, and the module heads and copper cables cannot be separated.
Direct Attach Cables (DACs) in Data Center Applications: Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are a type of high-speed cable used to connect servers, storage devices, and network equipment within data centers. They offer advantages such as low latency, high bandwidth, and low cost, making them widely used in data centers. Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are typically used for short-distance data transmission, such as within server racks or between adjacent racks. They can replace traditional fiber optic cables, providing higher bandwidth and lower latency, thereby improving data center performance and efficiency. Direct Attach Cables (DACs) can also be used to connect storage devices, such as SAN (Storage Area Network) and NAS (Network Attached Storage). They provide higher transmission speeds and lower latency, improving the performance and reliability of storage devices.
High-speed transmission is one of the biggest advantages of Direct Attach Cables (DACs). It supports data transfer rates of up to 100Gbps, which is significantly faster than traditional copper cables. This allows it to meet the high-speed data transmission demands of data centers, improving their efficiency and performance.
•High performance: Suitable for short-distance cabling in data centers, with a wide range of applications and strong integration and switching capabilities.
•Energy-saving and environmentally friendly: The Direct Attach Cables (DACs) uses a copper core, and copper cables have excellent natural heat dissipation, making them energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
•Low power consumption: Direct Attach Cables (DACs) consume little power. Passive cables require no power supply; active cables typically consume around 440mW.
•Low cost: Copper cables are significantly cheaper than fiber optic cables, and using high-speed copper cables can greatly reduce the overall cabling costs of a data center.
•Supports hot-swapping: Supports hot-swapping functionality, allowing for plugging and unplugging devices while the system is running, without needing to shut down the equipment, thus improving the flexibility and scalability of the data center.
AOC Cables are an abbreviation for Active Optical Cables, which refer to communication cables that require external power to convert electrical signals into optical signals, or optical signals into electrical signals during communication. The transceivers at both ends of the cable provide photoelectric conversion and optical transmission functions. The advantages of Active Optical Cables (AOCs) are:
•Wider bandwidth: No equipment upgrades are needed, and it offers a throughput of up to 40Gbps.
•Low electromagnetic interference: Because optical fiber is a dielectric material, it is not easily affected by electromagnetic interference.

•Different transmission media – Direct Attach Cables (DACs) use copper cables to transmit electrical signals, while Active Optical Cables (AOCs) use optical fibers to transmit optical signals.
•Power consumption and transmission distance different – Active Optical Cables (AOCs) have higher power consumption but support longer transmission distances (up to 100 meters); Direct Attach Cables (DACs) have lower power consumption and are suitable for short-distance transmission (usually no more than 10 meters).
•Different application – Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are commonly used for interconnecting devices within the same rack, while Active Optical Cables (AOCs) are suitable for long-distance, high-speed interconnections between different racks.
When choosing between Direct Attach Cables (DACs) and Active Optical Cables (AOCs) cables, the decision should be based on the specific application scenario, performance requirements, and budget. Direct Attach Cables (DACs) are the preferred choice for short-distance interconnections due to their low cost and low power consumption. Active Optical Cables (AOCs), on the other hand, are widely used in applications requiring high-speed data transmission over long distances, thanks to their advantages in long-distance transmission and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Direct Attach Cable (DAC) testing primarily focuses on frequency-domain parameters (such as S-parameters), time-domain parameters (TDR/TDT), and multi-port crosstalk evaluation.
Because Active Optical Cable (AOC) contain multiple active components, such as Retimers, CDRs, and O/E converters, a time-domain response excitation method is required to simulate signal transmission under realistic transmission conditions and to perform tests for jitter and bit error rate.
Data centers are the cornerstone of AI (artificial intelligence) and machine learning development, and Active Optical Cables (AOCs) and Direct Attach Cables (DACs), as a high-speed interconnect technology, provide crucial support for AI data centers! Whether for interconnecting GPU clusters, servers, or switches, Active Optical Cables (AOCs) and Direct Attach Cables (DACs) help data centers achieve higher data rates. Let's look forward to the continuously growing demand for high-speed interconnects and the testing challenges that come with it. Please contact us at Email sales@unitekfiber.com, if you have any inquiry or need any need.
+86-755-21034367



