DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) transceiver modules are optical devices that leverage DWDM technology to combine multiple optical signals of varying wavelengths onto a single optical fiber, greatly enhancing fiber capacity. These optical transceivers are mainly deployed in long-distance, high-capacity backbone networks and metropolitan area networks to meet growing bandwidth demands. They transmit data using closely spaced wavelengths (such as 0.4nm, 0.8nm, 1.6nm) and offer features like pluggable, tunable, and high-speed transmission, supporting distances over 100 kilometers.
Compared to ordinary fiber transceivers, DWDM fiber optic transceivers have the following differences:
DWDM fiber transceivers employ wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology, enabling the transmission of multiple optical signals using different wavelengths over the same optical fiber. Each signal occupies a different wavelength, allowing multiple data streams to be transmitted in parallel within the same fiber, thus significantly improving fiber optic efficiency. Regular fiber optic transceivers typically transmit only a single optical signal and cannot utilize multiple wavelengths for multiplexing. Therefore, during transmission, the fiber's capacity is limited and bandwidth cannot be extended by wavelength, thus constrained by transmission capabilities.
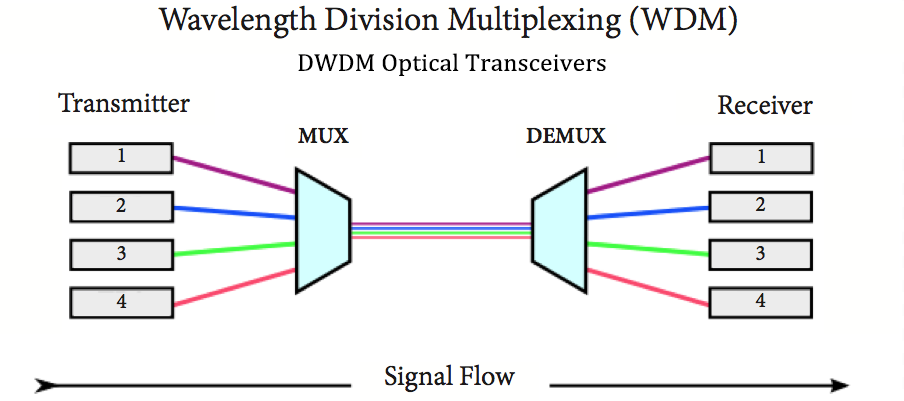
DWDM optical transceivers can transmit multiple optical signals of different wavelengths simultaneously on the same optical fiber. Therefore, the transmission capacity of a single fiber is greatly increased, supporting high-speed data transmission of tens or even hundreds of Gbps. With the multiplexing of signals of different wavelengths, DWDM significantly increases the bandwidth utilization of the optical fiber. Regular optical transceivers have relatively limited transmission capacity, generally only able to transmit data using a single wavelength. Even when transmitting through multiple fibers, the total bandwidth is still limited by the transmission capacity of each fiber, unable to reach the high bandwidth levels of DWDM fiber optic transceivers.

DWDM technology allows signals to be transmitted in parallel at different wavelengths, making DWDM transceiver modules particularly outstanding in long-distance transmission. Transmission distances can typically reach tens or even hundreds of kilometers, and it supports optical amplifiers to enhance the signal and reduce signal loss due to fiber attenuation, making it suitable for backbone networks and remote connections. Regular transceivers have shorter transmission distances, typically within a few kilometers. For long-distance transmission, signal attenuation is significant, requiring additional repeater equipment.
DWDM fiber transceivers offer higher spectral efficiency, enabling multi-channel transmission using different wavelengths within the same optical fiber. Each wavelength can carry an independent data stream, and this compact wavelength spacing (e.g., 0.4nm, 0.8nm, 1.6nm) maximizes the utilization of fiber resources. Regular optical transceivers, on the other hand, can only use a single wavelength for transmission and cannot utilize multiple wavelengths for parallel transmission. Therefore, their spectral efficiency is lower, typically limiting data transmission to lower bandwidths.
Because DWDM fiber optic transceivers enable wavelength division multiplexing, they significantly reduce the number of optical fibers required. During network construction, this reduction in fiber optic cabling and equipment costs leads to substantial lower construction and maintenance costs. The high capacity and long-distance transmission capabilities of DWDM optical transceivers allow a single network to cover a wider area.
However, regular fiber transceivers, which cannot achieve wavelength division multiplexing, typically require more fiber resources to expand bandwidth. Network expansion and construction necessitate more hardware and infrastructure, resulting in higher costs compared to DWDM networks. Achieving the same bandwidth requirements may necessitate laying more fiber optic cables and increasing equipment investment.
DWDM optical transceivers achieve multiplexed transmission through wavelength division multiplexing technology, improving the transmission capacity and distance of fiber optic networks while reducing network construction costs. DWDM fiber transceivers have broad application prospects in long-distance communication and high-capacity transmission scenarios. As a leading supplier in the industry, UnitekFiber offers a wide range of high-quality optical transceivers to meet diverse network needs. Whether in data centers, enterprise networks, or 5G communications, UnitekFiber provides advanced fiber optic solutions.
+86-755-21034367



