In optical transceiver, the terms "flat-top" and "heatsink-top" usually refer to two different structural designs of the optoelectronic device:
A flat-top structure typically refers to the top structure of the laser or optical emitter in an fiber optic transceiver being flat. This design allows light to propagate and focus more easily, facilitating more efficient transmission of optical signals in optical fibers or other transmission media. The flat-top design can improve light coupling efficiency and transmission efficiency, and is commonly found in some high-performance optical communication or optical sensing applications.
A heatsink-top structure typically refers to a design where the top of a laser or optoelectronic device incorporates a heatsink. These heatsinks are commonly used to effectively dissipate heat, keeping the device's operating temperature within a safe range. In high-power or high-density applications, devices may generate a significant amount of heat, which needs to be transferred to the surrounding environment via the heatsink to prevent overheating and damage. Therefore, heatsink design is crucial for the long-term stable operation of transceiver modules.
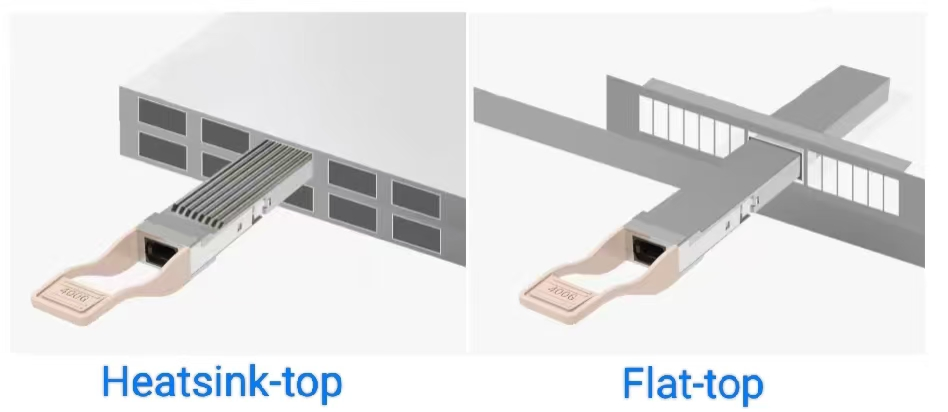
As transmission speeds increase, optical transceivers are becoming smaller, and the demands on internal optical components are becoming higher. Solving the heat dissipation problem is therefore essential. Both flat-top and heatsink-top designs for transceiver modules have their advantages. The best choice depends mainly on the transmission speed, interface type, packaging method, and specific application scenarios and requirements.
Transmission distance and data rate requirements: If your application requires long-distance, high-speed transmission, a flat-top structure may be more suitable because it helps improve light coupling efficiency and transmission efficiency. For short-distance or low-speed transmission, a heatsink-top structure can be considered.
Thermal Management Requirements: If your application involves lasers or optoelectronic devices that handle high power or high energy density, then a heatsink-top structure may be crucial. This is because it facilitates efficient heat dissipation, ensuring stable module operation and preventing overheating that could lead to performance degradation or damage. Good thermal management is especially critical in applications such as high-power optical communication or LiDAR.
Cost and Complexity: The flat-top version of the fiber transceiver has a simpler design without additional heatsink structures, as it primarily focuses on light transmission efficiency. The heat sink top structure, on the other hand, may require a more complex design and manufacturing process to ensure good heat dissipation performance. Therefore, you need to weigh these two options when considering cost and complexity.
Environmental conditions: Consider the environmental conditions in which your application will operate. If the ambient temperature is high or there is a possibility of being affected by other heat sources, good heat dissipation capabilities may be more important.
Reliability and stability requirements: If your application requires high reliability and long-term stable operation of the components, then choosing a heatsink design that provides good thermal management may be more suitable.
In the 800G OSFP series, the SR8, DR8, and 2FR4 transceivers all utilize a heatsink-top design to ensure stable operation and efficient heat dissipation during high-speed data transmission. The 400G OSFP SR4 and DR4 optical transceivers, on the other hand, use a flat-top design, suitable for applications with relatively lower heat dissipation requirements.
The transceivers with heatsink-top are particularly suitable for switch equipment requiring high heat dissipation efficiency, including Quantum-2 InfiniBand switches and Spectrum-4 Ethernet switches. When processing large amounts of data, these heatsink-top transceiver modules provide the necessary thermal management.
Flat-top slots are commonly used in adapters and data processing units (DPUs), such as the ConnectX-7 InfiniBand adapter card and the BlueField-3 DPU, their flat-top design, combined with heatsinks, helps meet the cooling requirements of these devices under various operating conditions.
The flat-top version and the heatsink-top version have the same internal structure, but the heatsink-top version is taller due to the inclusion of a heatsink. In terms of power dissipation, the OSFP fiber optic transceiver integrates the heatsink within the module casing and has a larger heat dissipation surface area than the QSFP-DD fiber transceiver, resulting in optimal thermal contact between the heat-dissipating components and the heatsink, and superior heat dissipation performance compared to the QSFP-DD transceiver.
Therefore, when choosing fiber transceivers, it is necessary to consider all these factors comprehensively and select the product that best suits your needs. UnitekFiber offers 400G fiber optic transceivers with both flat-top and heatsink-top. Please feel free to contact us for more information!
+86-755-21034367



