With the advent of the information age of human society, the demand for communication is accelerating. The rapid development of various new services (especially high-speed data and video services) places higher requirements on the bandwidth (or capacity) of the communication network. In order to adapt to the continuous increase of the transmission capacity of the communication network and meet the requirements of network interactivity and flexibility, various multiplexing technologies have been produced.
In addition to the well-known time division multiplexing (TDM) technology in optical fiber communication systems, other multiplexing technologies have appeared, such as optical time division multiplexing (OTDM), optical wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), and optical frequency division multiplexing ( OFDM) and Subcarrier Multiplexing (SCM) technology. Here we mainly describes the basic technology of WDM.
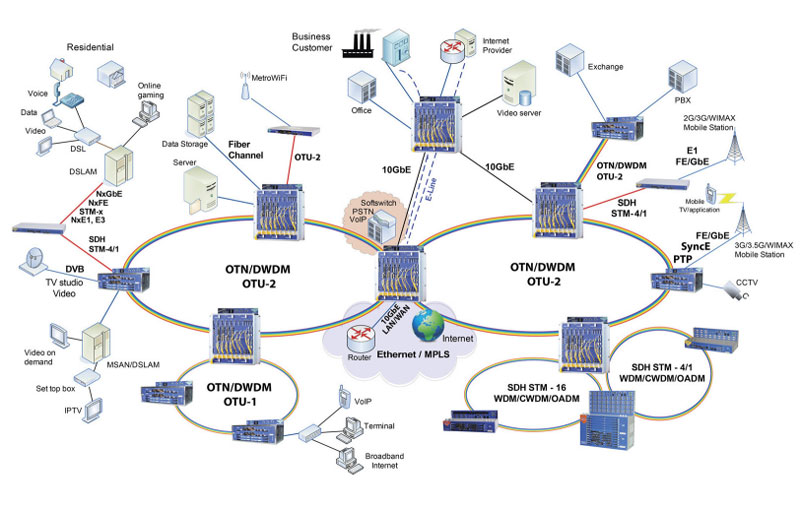
Generally speaking, WDM system is mainly composed of the following five parts: optical transmitter, optical relay amplifier, optical receiver, optical monitoring channel and network management system.
The optical transmitter is the core of the WDM system. According to ITU-T recommendations and standards, in addition to the special requirements for the center wavelength of the transmitting laser in the WDM system, it also needs to be based on the different applications of the WDM system (mainly the type of transmission fiber and Electrical relay transmission distance) to select a transmitter with a certain chromatic dispersion tolerance. At the transmitting end, the optical signal output from the terminal device (such as an SDH terminal) is first converted into an optical signal with a stable specific wavelength by using an Optical Transform Unit (OTU) that conforms to the G.957 recommendation. The multi-path optical signal is synthesized by a multiplexer, and then the multi-path optical signal is amplified and output through an Booster Amplifier (BA).
After long distance transmission from optical fiber (80-120km), it is necessary to perform optical relay amplification on optical signals. The optical amplifiers currently used are mostly Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers(EDFAs). In WDM system, the gain flattening technology must be adopted to make EDFA have the same amplification gain for optical signals of different wavelengths. At the same time, it is necessary to consider the situation that different numbers of optical channels work at the same time, which can ensure that the gain competition of the optical multiples does not affect transmission performance. In application, EDFA can be used as "line amplifier (LA)", "Booster Amplifier (BA)" and Pre-amplifier (PA)" according to the specific situation.

At the receiving end, an optical pre-amplifier (PA) amplifies the main channel optical signal that is attenuated through transmission, and uses a demultiplexer to divide the optical channel of a specific wavelength from the main channel optical signal. The receiver must not only meet the requirements of general receivers for optical signal sensitivity, overload power and other parameters, but also be able to withstand signals with certain optical noise and have sufficient electrical bandwidth performance.
The main function of the optical monitoring channel is to monitor the transmission status of each channel in the system. At the transmitting end, insert the optical monitoring signal with a wavelength of 1510nm generated by this node, and combine the output with the optical signal of the main channel. At the receiving end, the received optical signal is demultiplexed, and an optical monitoring signal with a wavelength of (1510 nm) and an optical signal of a service channel are respectively output. Frame synchronization bytes, service bytes, and overhead bytes used by the network management are transmitted through the optical monitoring channel.

The network management system transmits overhead bytes to other nodes or receives overhead bytes from other nodes to manage the WDM system through the physical layer of the optical monitoring channel, and implements functions such as configuration management, fault management, performance management, security management, and management with upper layers Systems (such as TMN) are connected.
If you neen more information or support on fiber optical products, please don’t hesitate to contact us sales@unitekfiber.com, we will try our best to support you.
+86-755-21034367