The latest research report from the market research company Omdia stated that after a sharp decline in operator spending in 2019 and the spread of the global epidemic in 2020, the cable broadband access equipment market is expected to rebound and reach 1 billion dollar in 2025 .
What drives this prediction is the next-generation technology in the front-end and external deployment space. Revenue from centralized access equipment will decline during 2018-2025, with a compound annual growth rate of -6%, and it will fall to US$656 million by 2025. The growth of cloud-based CMTS/CCAP offsets the further decline in this segment, and it is expected that this part of the growth will be very significant throughout the forecast period. Distributed access equipment is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 37% during 2018-2025. During the forecast period, shipments in this emerging segment will reach commercial levels, and revenue will be close to US$342 million by 2025.
North America will still be the main consumer of Cable broadband access equipment, accounting for 65% of total equipment revenue. Although the overall market will rebound from the downward trend in 2019-2020, the level of expenditure will show a compound annual growth rate of -1% during 2018-2025.
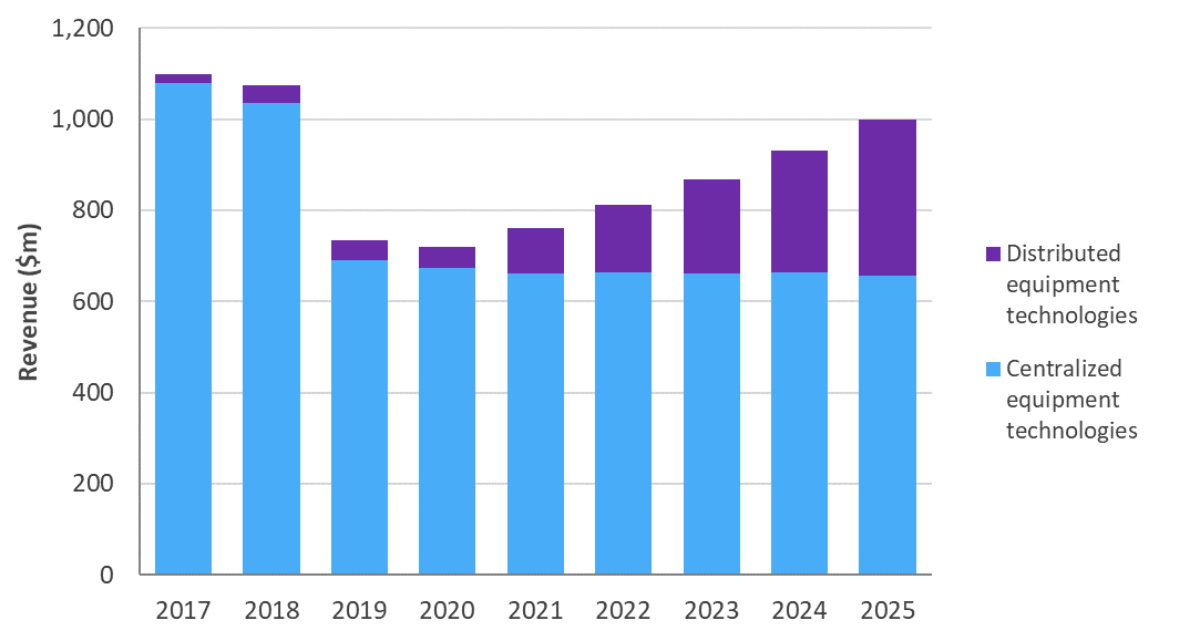
Figure 1:The market of Cable broadband access equipment in each major segment, 2017-2025.
Source: "Omdia 2020-2025 Cable Broadband Access Equipment Forecast".
This research report highlights some forecast trends in the global Cable broadband access equipment market.
The next generation transformation will drive the market rebound.
After the sharp drop in operator spending in 2019 and the further aggravation of the new crown epidemic in 2020, the cable broadband access equipment market rebounded sharply during the forecast period. The main driving force during the forecast period is the next-generation Cable broadband access technology, as shown in Figure 2.
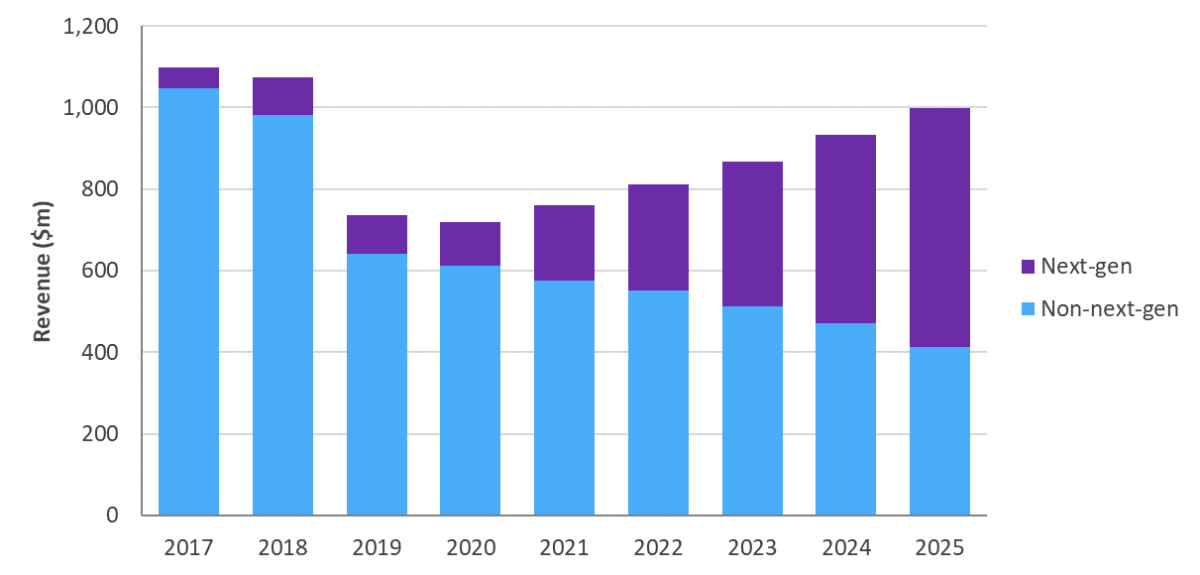
Figure 2: The market of next-generation and non-next-generation Cable broadband access equipment , 2017-2025.
Source: Omdia.
The market of non-next-generation equipment includes traditional, centralized CMTS/CCAP equipment. During the forecast period, non-next-generation devices will continue to account for a large portion of Cable broadband access equipment spending. However, traditional CMTS/CCAP will only account for 41% of total revenue by 2025. In contrast, traditional CMTS/CCAP accounted for more than 90% of all Cable broadband access equipment revenue in 2018. This shift reflects the fact that Cable operators have invested capital expenditures on improving front-end efficiency, and have gained support for cloud-based CMTS and distributed access architecture (DAA).
As shown in Figure 3, the compound annual growth rate of next-generation Cable broadband access equipment during 2018-2025 will reach 30%, and revenue will be close to US$584 million by 2025. Next-generation technologies include cloud-based CMTS/CCAP, RPD/RMD equipment and racks, and digital optical fiber nodes. In general, these technologies represent a shift from traditional Cable network infrastructure placed in cramped and expensive front-ends to collaborative architecture. The previously isolated aspects of the network can be flexibly combined through cloud and software configuration. This report further defines the forecast of each next-generation technology.
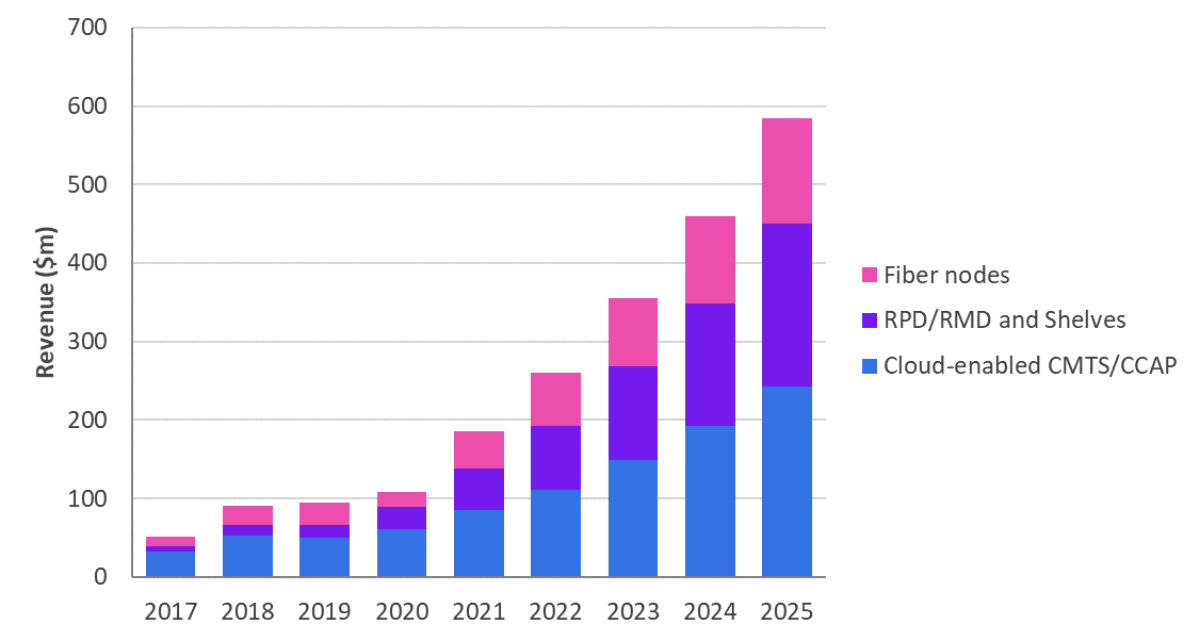
Figure 3: Divided the next-generation Cable broadband access equipment market by equipment type, 2017-2025.
Source: Omdia.
Transfer Centralized Equipment Revenue to Cloud-enabled Technology
During the forecast period, operators will focus on the transition to DAA, which requires capital expenditures to be shifted from centralized equipment to other locations. As shown in Figure 4, the global revenue of centralized Cable broadband access equipment is expected to drop to US$656 million in 2025. Nevertheless, they will continue to optimize the front end through cloud technology and SDN/NFV.
During the forecast period, Omdia focuses on two centralized equipment revenue areas:
lCMTS/CCAP: The archirecture of traditional and centralized ; the hardened CMTS/CCAP equipment in the front end or hub.
lCloud-based CMTS/CCAP: Contains the next-generation software platform and virtualization functions related to DOCSIS configuration, as well as any basic hardening equipment required.
Cloud-based CMTS/CCAP revenue is expected to increase to US$242 million in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 32% during 2020-2025, accounting for 37% of centralized equipment revenue in 2025. Although this growth is not enough to offset the overall decline in centralized access equipment during the forecast period, in the next few years, cloud-based CMTS/CCAP will eventually surpass traditional CMTS/CCAP. This will happen when cable operators strive to improve the efficiency of front-end, and when cable suppliers transfer their cable operator customers to licensing and "purchase on demand" models to support further revenue growth.
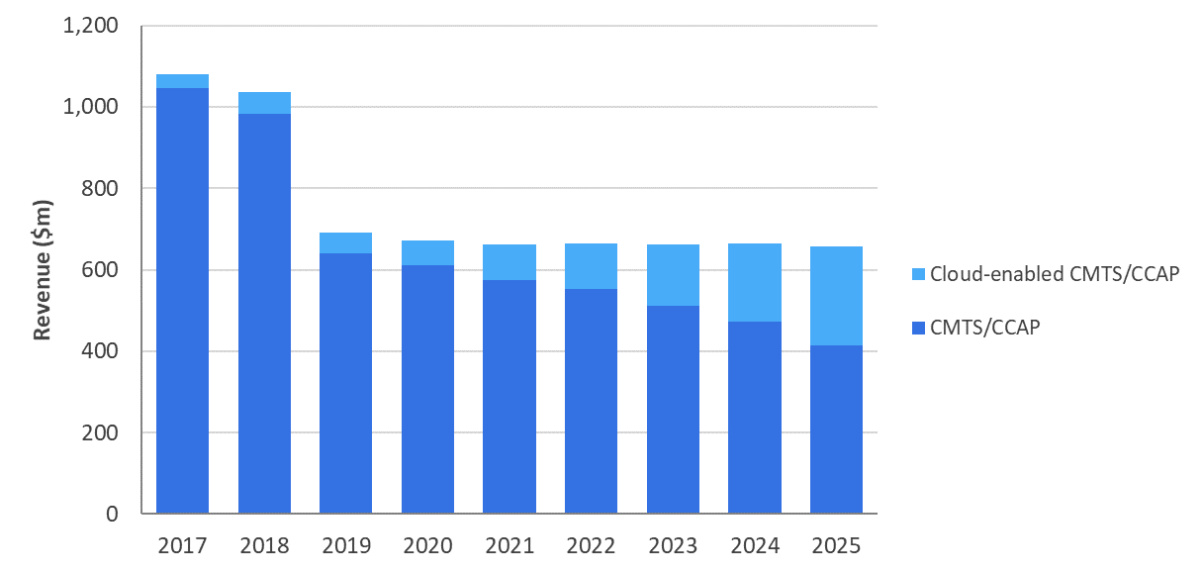
Figure 4: Global centralized cable broadband access equipment revenue, 2017-2025.
Source: "The forecast of Omdia 2020-2025 Cable Broadband Access Equipment ".
After switching to DOCSIS 4.0, CableLabs completed the final specifications in early 2020. Therefore, it still need some time for the chips to be used in the supplier's development of equipment. Omdia predicts that DOCSIS 4.0 equipment will begin shipping in 2023, and commercial upgrades will begin in 2024. Some Cable operators will hope to implement DOCSIS 4.0 as soon as possible to achieve higher bandwidth, while other operators will be satisfied with their relatively newly upgraded DOCSIS 3.1 network capacity.
The distributed access equipment will develop from new type to commercial type
In the years after the epidemic, many cable operators focused on broadband will begin to switch to DAA, not only to improve the operating cost efficiency of the front-end , but also to move their networks toward end-to-end automation and control.
During the forecast period, Omdia will focus on two parts of defined distributed equipment revenue :
lRemote PHY/MACPHY equipment and rack (RPD/RMD), including equipment related to remote PHY/long-distance MACPHY equipment. The remote PHY/remote MACPHY device can be placed in a digital optical fiber node, or deployed in a chassis located in the hub or front end.
lThe optical fiber node is composed of digital optical fiber nodes. These nodes use 10GBE digital optical fiber to coaxial equipment and accommodate RPD/RMD equipment.
Cable operators are slow to adopt equipment in this market segment, partly because they are hesitant to migrate to DOCSIS, such as Node+0 and Extended Spectrum DOCSIS, which will affect external deployment space strategies. The spread of the global epidemic in 2020 has exacerbated this trend of market slowdown. With the finalization of the DOCSIS 4.0 specification, Omdia expects DAA revenue to begin to be realized in 2021. As shown in Figure 5, global distributed access equipment revenue is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 49% during 2020-2025, and reach 342 million dollars in 2025.
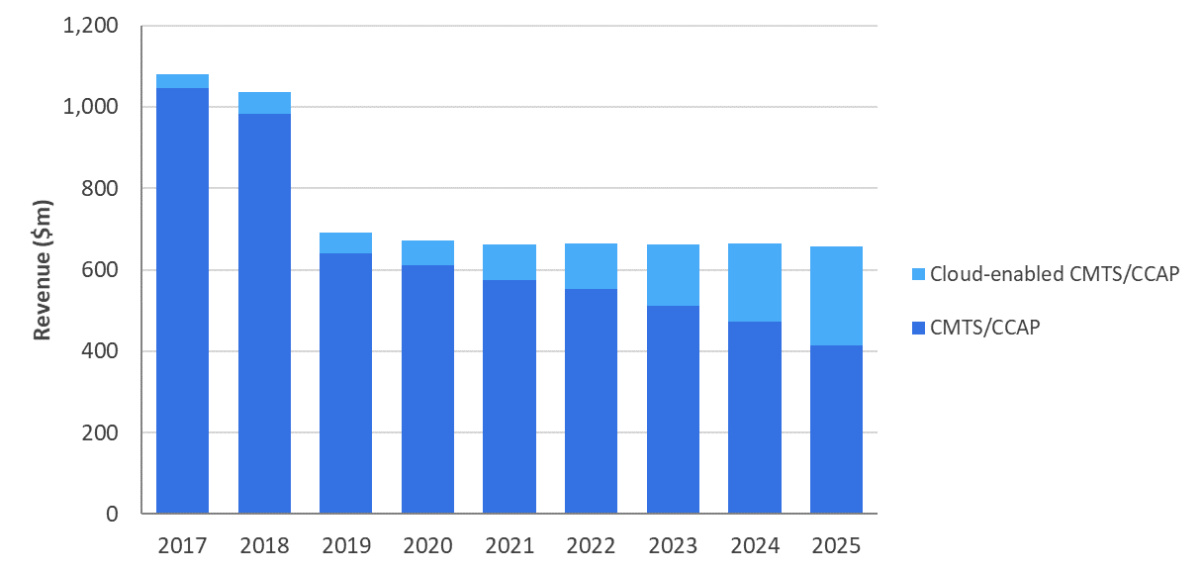
Figure 5: Global Distributed Cable Broadband Access Equipment Revenue, 2017-2025.
Source: "The forecast of Omdia 2020-2025 Cable Broadband Access Equipment ".
In addition, the field of distributed access equipment will be driven by the contractual obligations between existing cable operators and suppliers. Although RPD/RMD equipment and racks will account for 61% of all distributed equipment revenue by 2025, digital fiber nodes are expected to continue to grow as Cable operators implement fiber in-depth strategies.
North America Ranks First in the Consumption of Cable Access Equipment
During the entire forecast period, North America will consume the largest proportion of Cable broadband access equipment shipments, and will reach 65% of global shipments by 2025. North America is different from other regions because most broadband users receive services through Cable Modem. Cable operators have undergone extensive integration through mergers and acquisitions, further restricting competition. Relying on the advantages of the original infrastructure, North American Cable operators will continue to utilize their HFC networks through spectrum upgrades, switch to cloud-based CMTS/CCAP, and introduce optical fibers deeper into the external space. As shown in Figure 6, Cable broadband access equipment spending in North America will reach 648 million U.S. dollars by 2025, which is a substantial increase from the forecast of 397 million U.S. dollars in 2020 when the global epidemic is spreading, and the compound annual growth rate during the period will reach 10%.
In the EMEA (Europe, Middle East and Africa) region, from the end of 2019 to the beginning of 2020, despite the spread of the global epidemic, operators in this region are undergoing DOCSIS 3.1 upgrades. Omdia predicts that broadband access equipment revenue will fall to 139 million dollars in 2020. However, after the coronavirus, cable upgrades in the region will continue, especially in Western Europe. Several large cable operators in the region are focusing on cloud-based CMTS/CCAP upgrades. In the EMEA region, this market segment will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 30% during 2020-2025, and reach $40 million in 2025. As many Cable vendors switch to "pay-as-you-go" licensing model of capacity and software, this part of the market is expected to grow further in the next ten years and beyond.
In Asia and Oceania, the overall Cable broadband access equipment revenue will remain stable during 2020-2025, at approximately US$83 million per year. However, under this stability, the situation in each country is different. In order to remain competitive, some Cable operators will switch to PON networks during the forecast period, while other operators will continue to invest in their coaxial Cable networks to offset the regional decline. China will continue to focus on building a huge PON access network across the country. Although many cable operators centered on broadcast and television provide broadband on their HFC networks, compared with major cities that use PON (PON is also used for non-residential purposes in cities), these rural networks will still be relatively slow.
In Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC), Cable broadband access equipment revenue is expected to increase from 100 million dollars predicted in 2020 to 115 dollars million by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 3% during the period. During the forecast period, revenue from centralized equipment will remain stable at approximately US$96 million per year. In this market segment, the region's revenue will shift from centralized CMTS/CCAP to cloud-based CMTS/CCAP. By 2025, cloud-based CMTS/CCAP will account for more than 25% of centralized equipment revenue, and this number will continue to grow in the next ten years. Although the region will switch to DAA, concerns about the security of the external deployment space indicate that the use of RPD/RMD racks in the hub may be more than the on-site intelligent fiber node pairing RPD/RMD.
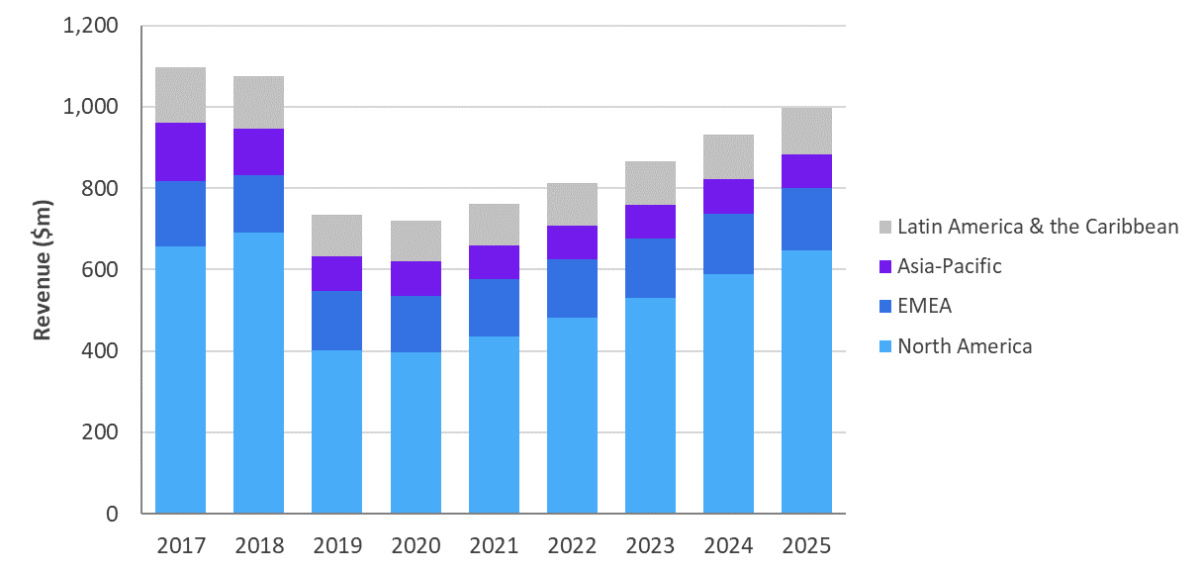
Figure 6: The market of Cable broadband access equipment by region.
Source: " Omdia's forecast for Cable broadband access equipment from 2020 to 2025".
What's next? ——The Cable field will continue to grow into the 2030s
Jaimie Lenderman, senior technical analyst for Omdia service provider, and Julie Kunstler, chief technical analyst for Omdia service provider, said that as the cable broadband access equipment market resumes growth after the epidemic, cable operators will continue to work hard to transform existing networks to maintain competitiveness for optical fiber products and meet customer broadband needs. By adopting cloud-enabled front-end equipment and distributed access equipment, cable operators can become more agile and decentralized, moving toward automation and virtualization. This transition will require time and migration path. The timing will depend on several factors, including operators, regions, competitive landscape and customer needs.
[Note: Omdia was formed by the merger of Informa Tech's research departments (Ovum, Heavy Reading, and Tractica) with the acquired IHS Markit technical research department. It is a world-leading technical research organization. ]
+86-755-21034367



