
In data centers, local area networks (LANs), and short-distance communication scenarios, multimode optical patch cord enable high-speed data transmission. With their advantages of multipath transmission and low cost, they have become a core component for high-speed data transmission. This article will unveil the mysteries of multimode fiber patchcord from four dimensions: technical principles, classification, application scenarios, and selection guidelines.
The core of multimode patch cord lies in their multimode transmission characteristics. Unlike single-mode fiber, which allows only a single optical path for propagation, multimode fiber has a larger core diameter (typically 50μm or 62.5μm), accommodating multiple optical modes for simultaneous transmission. This characteristic allows optical signals to refract at different angles within the fiber, forming multiple propagation paths, thus enabling high-bandwidth data transmission over short distances.
However, multipath transmission also presents challenges—modal dispersion. Different modes of light travel at different speeds during transmission, leading to signal distortion and loss of quality. To address this issue, multimode patch cord reduce modal dispersion by optimizing the core refractive index distribution (e.g., in graded-index fiber) while limiting the transmission distance (typically from a few hundred meters to several kilometers) to balance bandwidth and stability.
Multimode patch cord can be classified into five categories based on performance: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5 fiber patch cords. Their core differences lie in mode bandwidth and transmission distance:
OM1 (62.5/125μm) fiber optic patchcord is an early type of multimode fiber patchcord with a bandwidth of 200MHz·km and a transmission distance of approximately 300 meters (850nm wavelength). Due to significant modal dispersion, it has been gradually replaced by high-performance models.

OM2 (50/125μm) fiber optic patchcord’ bandwidth was increased to 500MHz·km, transmission distance was increased to approximately 550 meters. It suitable for traditional local area networks, but insufficient for the demands of high-speed data centers.

OM3 (50/125μm, laser-optimized) fiber optic patchcord’ bandwidth reaches 2000MHz·km, supports 10Gbps transmission rate, and transmission distance of 300 meters (850nm). Due to its high cost-effectiveness, it has become a mainstream choice for data centers.

OM4 (50/125μm, ultra-laser-optimized) fiber optic patchcord’ bandwidth is further increased to 4700MHz·km, supporting 10Gbps transmission distance of 550 meters, or 40Gbps/100Gbps short-distance transmission. It is suitable for high-performance computing and cloud data centers.
OM5 (50/125μm, Wideband Multimode) fiber optic patchcord, the latest standard, supporting shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM) technology, can transmit in the 850-953nm wavelength range, with bandwidth expanding as technology upgrades, which is suitable for future high-speed network expansion.

Multimode fiber patchcords are widely used due to their advantages of short-distance transmission, high bandwidth and low cost. In the scenario of internal interconnection of data centers, they can realize high-speed data transmission between servers, storage devices and switches.
OM3/OM4 fiber optical patch cord support transmission rates of 40Gbps/100Gbps, capable of meeting the requirements of cloud computing and big data scenarios.

In the deployment of local area networks (LANs), they can be applied in enterprise parks, campus networks and office buildings to connect core switches with access layer devices, providing stable Gigabit and 10-Gigabit network access.
In the fiber-to-the-desk (FTTD) application scenarios of office environments, multimode fiber patchcord can directly transmit optical signals to workstations, supporting various high-bandwidth requirements such as high-definition video conferences and large file transfers.

Meanwhile, in the testing and maintenance scenarios for network device debugging and troubleshooting, they can serve as temporary connection tools to quickly verify the connectivity of links.
Multimode fiber patchcord also plays an important role in industrial automation. In factory workshops, multimode patch cords connect sensors, controllers, and actuators to enable real-time data acquisition and control.
Short distance (<300 meters): OM3/OM4 fiber optical patch cord can meet 10Gbps/40Gbps requirements.
Medium distance (300-550 meters): OM4 fiber optical patch cord is the preferred choice.
Future expansion: OM5 fiber optical patch cord will be used for compatibility with SWDM technology.
Multimode patch cord interfaces include LC, SC, and MPO. LC interfaces are the mainstream choice for data centers due to their small size and ease of insertion and removal; MPO interfaces are suitable for high-density cabling (such as 8-core, 12-core, 16-core 24-core, 48 cores parallel transmission).


Bending Radius: To avoid excessive bending that could break the fiber, a bending radius ≥ 10 times the fiber core diameter is recommended.
Tensile Strength: Choose optical patch cord with a Kevlar reinforcing core to improve tensile strength.
PVC sheath is suitable for indoor environments (low cost). For scenarios with high fire resistance requirements, LSZH (Low Smoke Halogen-Free) sheath is required.
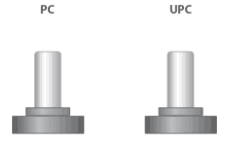
PC’ end face is suitable for general applications,its insertion loss is ≤0.3dB.
UPC with a flatter end face and a return loss of ≥50dB, it is suitable for high-definition video transmission.
With the advancement of 400Gbps/800Gbps Ethernet standards, multimode fiber optic patchcord is evolving towards higher bandwidth and lower loss. The combination of OM5 fiber and SWDM technology enables the transmission of multi-wavelength signals through a single fiber, significantly improving link capacity. Meanwhile, innovative designs such as flexible metal-armored fiber patchcord further enhance the adaptability of multimode fiber in industrial environments.
Multimode fiber optic jumpers, with their unique transmission characteristics, rich variety of options, and wide range of applications, have become the "best cost-effectiveness" for short-distance data transmission. Whether building high-speed data centers or optimizing enterprise LANs, choosing the right multimode fiber patchcord can provide a solid guarantee for network performance. In the future, with the continuous evolution of technology, multimode patch cord will continue to play the critical role in the field of optical communication.
As a professional fiber optic patchcord manufacturer, UnitekFiber provide types of high-quality multimode patch cord, such as indoor/outdoor fiber optic patchcord, FTTH drop cable fiber optic patchcord, uniboot fiber optic patch cord.


