
"Internet" has become a "necessity" for most contemporary people. Everyone often ridicules this phenomenon. The current data center is no longer just one or several computer rooms, but a group of data center clusters. In order to realize the normal work of various Internet services and application markets, the data centers are required to work together. The real-time massive exchange of information between data centers creates the demand for data center interconnection networks, and fiber optic communication has become a necessary means of interconnection.
Unlike traditional telecommunications access network transmission equipment, data center interconnection requires greater and more dense information transmission, which requires switching equipment to have higher speeds, lower power consumption, and more miniaturization. The core factor that determines whether these performances can be achieved is the fiber optical transceiver module.
What is an optical transceiver module?
The information network mainly uses optical fiber as the transmission medium, but at present calculation and analysis must also be based on electrical signals, and the optical transceiver module is the core device that realizes photoelectric conversion.
The core components of the optical transceiver module are composed of Transimitter (optical transmission sub-module),Receiver (optical reception sub-module) ,Transceiver (optical transceiver integrated module),electrical chip, passive devices such as lenses, splitters, and beam combiners and Peripheral circuit composition.
At the transmitting end: the electrical signal is converted into an optical signal by Transimitter, and then input to the optical fiber by the optical adapter. At the receiving end: the optical signal in the optical fiber is received by the Receiver through the optical adapter and converted into an electrical signal, and sent to the computing unit for processing.
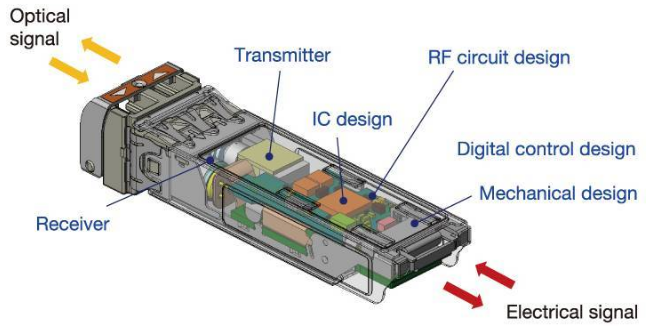
Schematic diagram of optical transceiver module
With the development of optoelectronic integration technology, the packaging form of the optical transceiver module has also undergone some changes. In the early stage of the optical transceiver module industry, the major telecommunication equipment manufacturers developed their own interfaces, and the interfaces were diverse and not universal, which resulted in the inability to interchange optical transceiver modules. For the development of the optical transceiver module industry, "Multi Source Agreement (MSA)" finally came into being. With the MSA standard, companies that independently focus on the development of Transceiver began to emerge, and the industry rose.
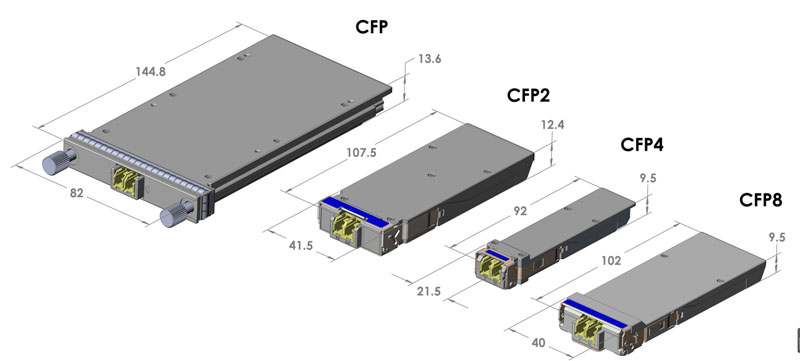
According to the package form,the optical transceiver module can be divided into SFP, XFP, QSFP, CFP, etc.
l SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) is a compact, pluggable fiber transceiver module standard for telecommunications and data communications applications, which can support a transmission rate up to 10Gbps.

l XFP (10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable) is a standard of small form factor pluggable fiber transceiver module of 10G rate that supports multiple communication protocols, such as 10G Ethernet, 10G Fibre Channel and SONETOC-192. XFP fiber transceivers can be used in the data communications and telecommunications markets and provide better power consumption characteristics than other 10Gbps transceivers.

l QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) is a compact, pluggable fiber transceiver standard, mainly used for high-speed data communication applications. According to the speed, QSFP can be divided into 1×40G QSFP, 4×10GQSFP+, 4×25G QSFP28 optical modules, etc. QSFP28 has been widely used in global data centers.

l CFP (Centum gigabits Form Pluggable) is a dense wavelength division optical communication module that based on a standardized, with a transmission rate of up to 100-400Gbps. The size of the CFP fiber transceiver module is larger than that of SFP/XFP/QSFP, and is generally used for long-distance transmission such as metropolitan area networks.
What are applications of Optical transceiver module in data center?
Data center communications can be divided into three categories according to connection types:
(1) From the data center to the user, it is generated by terminal user behaviors such as accessing the cloud to browse the web, send and receive emails and video streams;
(2) Data center interconnection, mainly used for data replication, software and system upgrades;
(3) The interior of data centre, it is mainly used for information storage, generation and mining. According to Cisco's forecast, data center internal communications account for more than 70% of data center communications. The great development of data center construction has given birth to the development of high-speed optical transceriver modules.
Data traffic continues to grow, and the trend of large and flat data centers promotes the development of optical modules in two aspects:
l Increase in transmission rate requirements
l Increase in quantity demand
At present, the global data center optical transceiver module demand has changed from 10/40G optical transceiver module to 100G/400G optical transceiver module.
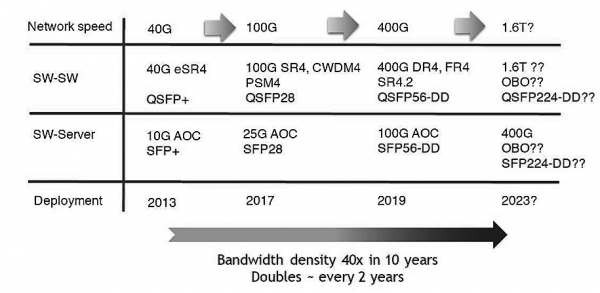
The evolution path of Alibaba Cloud optical modules
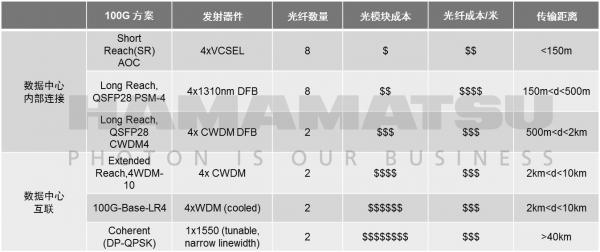
The large-scale trend of data centers has led to an increase in transmission distance requirements. The transmission distance of multi-mode fiber is limited by the increase in signal rate, and it is expected to be gradually replaced by single-mode fiber. The cost of an optical fiber link consists of two parts: an optical transceiver module and an optical fiber. There are also different applicable solutions for different distances. In terms of medium and long-distance interconnection required for data center communication, there are two revolutionary solutions born from MSA:
l PSM4(Parallel Single Mode 4 lanes)
l CWDM4(Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer 4 lanes)
Among them, PSM4 fiber usage is 4 times that of CWDM4. When the link distance is long, the cost of the CWDM4 solution is relatively low. From the following table, we can see the comparison of 100G optical module solutions for data centers:
Today, the implementation technology of 400G optical transceiver modules has become the focus of the industry. The main function of 400G optical transceiver modules is to increase the throughput of data and maximize the bandwidth and port density of the data center. Its future trend is to achieve wide-gain, low-noise, miniaturization and integration performance to meet the application requirements of next-generation wireless networks and ultra-large-scale data center communications.
The early 400G optical transceiver modules used the signal modulation method of 16-channel 25G NRZ (Non-Returnto Zero, non-return to zero)and adopted CFP8 package. The advantage is that it can borrow the mature 25G NRZ signal modulation technology on 100G optical transceiver modules, but the disadvantage is that 16 signals are required for parallel transmission, and the power consumption and volume are relatively large, which is not suitable for data center applications. In the current 400G optical module, 8 channels 53G NRZ or 4 channels 106G PAM4 (4 Pulse Amplitude Modulation, 4-level pulse amplitude modulation) signal modulation methods are mainly used to realize 400G signal transmission.
In terms of module packaging, QSFP or QSFP-DD is used, both of which can provide 8 electrical signal interfaces. In comparison, QSFP-DD package size is smaller, more suitable for data center applications; QSFP package size is slightly larger, more power consumption, more suitable for telecommunications applications.
100G/400G optical transceiver module solutions
We have briefly introduced the implementation of 100G and 400G optical transceiver modules. The schematic diagrams of the 100G CWDM4, 400G CWDM8, and 400G CWDM4 solutions can be seen below:
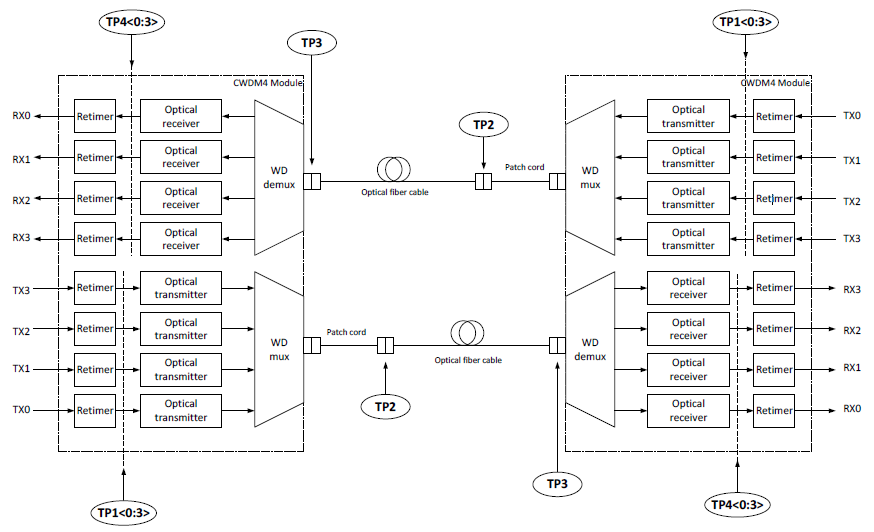
The schematic of 100G CWDM4
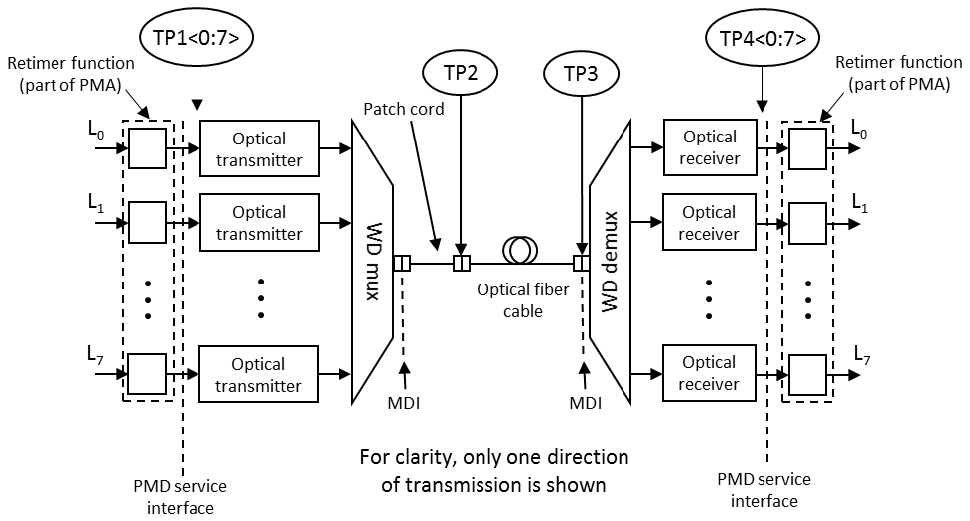
The schematic of 400G CWDM8
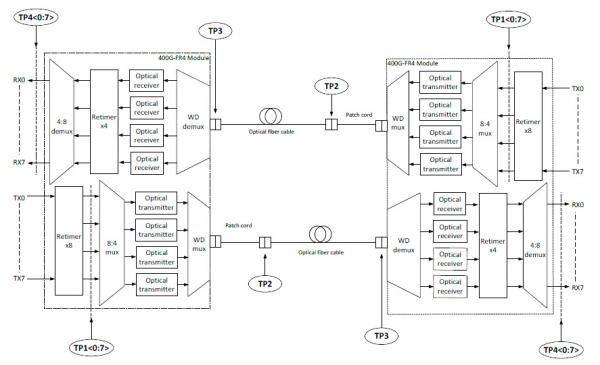
The schematic of 400G CWDM4
As an optoelectronic company with more than 10 years of experience, Unitekfiber has extensive experience in the development and production of optical communication devices. UnitekFiber guarantees the quality of its products and continuously provides quality products to the world. Next, we also hope to provide better possibilities for the development of optical communication and data center communication optical modules through continuous improvement of our own technology.
If you need more information or support on fiber optical products, please don’t hesitate to contact us sales@unitekfiber.com, we will try our best to support you.
+86-755-21034367



